|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| doc | ||
| hosts | ||
| keys | ||
| modules | ||
| overlays | ||
| .git-blame-ignore-revs | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .sops.yaml | ||
| README.md | ||
| deploy-flake.sh | ||
| flake.lock | ||
| flake.nix | ||
| host-registry.nix | ||
| packages.nix | ||
| users.nix | ||
README.md
Setup
Add this repo to your local Nix registry
As an alternative to a local checkout, always pull the latest code from this repo.
nix registry add c3d2 git+https://gitea.c3d2.de/C3D2/nix-config
This enables nix commands to find this Flake given the c3d2#
prefix in some arguments.
Working with this repo
If you checked out this git repository for working on the code,
replace c3d2# with .# and run commands from the repository root.
Don't forget to git add new files! Flakes require that.
The secrets repo
Make sure you have access.
Install Nix Flakes
Nix Flakes ist gegenwärtig bei Nix (Version 20.09) noch keine standardmäßige Funktionalität für Nix. Die Bereitstellung der Kommandos für Nix Flakes müssen als experimentelle Funktionalität für das Kommando ''nix'' festgelegt werden, um sie verfügbar zu machen.
Set some configuration (do this only once):
echo 'experimental-features = nix-command flakes' >> ~/.config/nix/nix.conf
Permanent System with Nix Flakes
set this to your NixOS configuration:
{ pkgs, ... }: {
nix = {
extraOptions = "experimental-features = nix-command flakes";
};
}
Deployment
Deploy a NixOS system from this Flake locally
Running nixos-rebuild --flake c3d2 switch on a machine should be sufficient
to update that machine to the current configuration and Nixpkgs revision.
Deploy to a remote NixOS system with this Flake
For every host that has a nixosConfiguration in our Flake, there are
two scripts that can be run for deployment via ssh.
-
nix run .#glotzbert-nixos-rebuild switchCopies the current state to build on the target system. This may fail due to eg. container resource limits.
The target must already be a nixFlakes system.
-
nix run .#glotzbert-nixos-rebuild-local switchBuilds locally, then uses
nix copyto transfer the new NixOS system to the target.Help! It's needlessly rebuilding stuff that already runs on the target? If so, use
nix copyto transfer where/run/current-systempoints to to your build machine.
Remote deployment from non-NixOS
A shell script that copies the current working tree, and runs
nixos-rebuild switch on the target:
./deploy-flake.sh hydra.hq.c3d2.de
It cannot not lookup hostnames in host-registry.nix. To avoid
deploying the wrong container on the unrelated DNS records, the script
always uses the hostname that is already configured on the target
system.
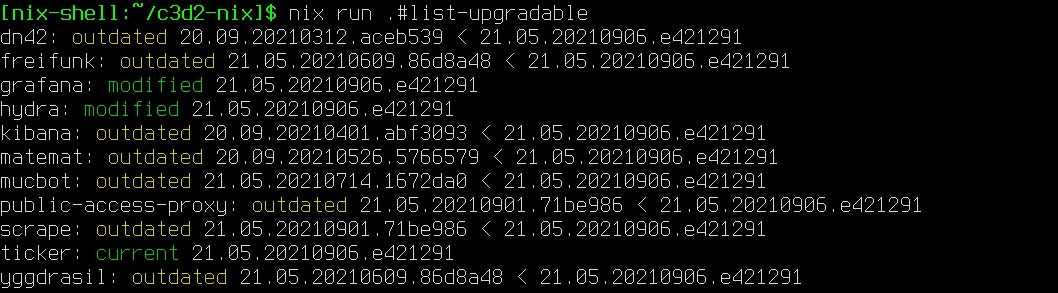
Checking for updates
nix run .#list-upgradable
Checks all hosts with a nixosConfiguration in flake.nix.
Update from Hydra build
The fastest way to update a system, a manual alternative to setting
c3d2.autoUpdate = true;
Just run:
update-from-hydra
Deploy a MicroVM
Building spaceapi remotely, and deploy
nix run .#microvm-update-spaceapi
Building spaceapi locally, and deploy
nix run .#microvm-update-spaceapi-local
Update MicroVM from our Hydra
Our Hydra runs nix flake update daily in the updater.timer,
pushing it to the flake-update branch so that it can build fresh
systems. This branch is setup as the source flake in all the MicroVMs,
so the following is all that is needed on a MicroVM-hosting server:
microvm -Ru $hostname
Cluster deployment with Skyflake
About
Skyflake provides Hyperconverged Infrastructure to run NixOS MicroVMs on a cluster. Our setup unifies networking with one bridge per VLAN. Persistent storage is replicated with Glusterfs.
Recognize nixosConfiguration for our Skyflake deployment by the
self.nixosModules.cluster-options module being included.
User interface
We use the less-privileged c3d2@ user for deployment. This flake's
name on the cluster is config. Other flakes can coexist in the same
user so that we can run separately developed projects like
dump-dvb. leon and potentially other users can deploy Flakes and
MicroVMs without name clashes.
Deploying
git push this repo to any machine in the cluster, preferably to Hydra because there building won't disturb any services.
You don't deploy all MicroVMs at once. Instead, Skyflake allows you to select NixOS systems by the branches you push to. You must commit before you push!
Example: deploy nixosConfigurations mucbot and sdrweb (HEAD is your
current commit)
git push c3d2@hydra.serv.zentralwerk.org:config HEAD:mucbot HEAD:sdrweb
This will:
- Build the configuration on Hydra, refusing the branch update on broken builds (through a git hook)
- Copy the MicroVM package and its dependencies to the binary cache that is accessible to all nodes with Glusterfs
- Submit one job per MicroVM into the Nomad cluster
Deleting a nixosConfiguration's branch will stop the MicroVM in Nomad.
Updating
TODO: how would you like it?
MicroVM status
ssh c3d2@hydra.serv.zentralwerk.org status
Debugging for cluster admins
Glusterfs
Glusterfs holds our MicroVMs' state. They must always be mounted or brains are split.
gluster volume info
gluster volume status
Restart glusterd
systemctl restart glusterd
Remount volumes
systemctl restart /glusterfs/fast
systemctl restart /glusterfs/big
Nomad
Check the cluster state
nomad server members
Nomad servers coordinate the cluster.
Nomad clients run the tasks.
Browse in the terminal
wander and damon are nice TUIs that are preinstalled on our cluster nodes.
Browse with a browser
First, tunnel TCP port :4646 from a cluster server:
ssh -L 4646:localhost:4646 root@server10.cluster.zentralwerk.org
Then, visit https://localhost:4646 for for full klickibunti.
Reset the Nomad state on a node
After upgrades, Nomad servers may fail rejoining the cluster. Do this to make a Nomad server behave like a newborn:
systemctl stop nomad
rm -rf /var/lib/nomad/server/raft/
systemctl start nomad
Secrets management
Secrets managment with PGP
Add your gpg-id to the .gpg-id file in secrets and let somebody reencrypt it for you. Maybe this works for you, maybe not. I did it somehow:
PASSWORD_STORE_DIR=`pwd` tr '\n' ' ' < .gpg-id | xargs -I{} pass init {}
Your gpg key has to have the Authenticate flag set. If not update it and push it to a keyserver and wait. This is necessary, so you can login to any machine with your gpg key.
Secrets Management Using sops-nix
Adding a new host
Edit secrets/.sops.yaml:
- Add an AGE key for this host. Comments in this file tell you how to do it.
- Add a
creation_rulessection forhost/$host/*yamlfiles
Editing a hosts secrets
Edit secrets/.sops.yaml to add files for a new host and its SSH pubkey.
# Enter the secrets flake
cd secrets
# Get sops
nix develop
# Decrypt, start en EDITOR, encrypt
sops hosts/.../secrets.yaml
# Push
git commit -a -m YOLO
git push origin HEAD:master
# Go back to this flake
cd ..
# Update flake.lock file
nix flake lock . --update-input secrets
Laptops / Desktops
This repository contains a NixOS module that can be used with personal machines
as well. This module appends /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts with the host keys of
registered HQ hosts, and optionally appends /etc/hosts with static IPv6
addresses local to HQ. Simply import the lib directory to use the module. As
an example:
# /etc/nixos/configuration.nix
{ config, pkgs, lib, ... }:
let
c3d2Config =
builtins.fetchGit { url = "https://gitea.c3d2.de/C3D2/nix-config.git"; };
in {
imports = [
# ...
"${c3d2Config}/modules/c3d2.nix"
];
c3d2 = {
isInHq = false; # not in HQ, this is the default.
mergeHostsFile = true; # Make entries in /etc/hosts form hosts.nix
enableMotd = true; # Set the login shell message to the <<</>> logo.
};
# ...
}